FLX app provides a basic File API to find, create, read, write, and delete files similar to APIs provided in Android and Java/Kotlin.
File API Functions

Creates the file specified by the file if it does not exists.
file– aFileobject
Returns: a Boolean value indicating if the creation succeeded.

Returns the application’s data directory. This directory does not require any read nor write permissions from the user.
Returns: a File denoting the data directory.

Deletes the file denoted by given file. If the file is directory then all the files contained by the directory are deleted – so be careful.
file– aFileobject
Returns: a Boolean value indicating if the deleting succeeded.

Tests if the given file exists
file– aFileobject
Returns: a Boolean value.

Creates a new File instance from a directory and a fileName string.
directory– aFileobject specifying the directoryfileName– the name of the file to be created as aString
Returns: a File object or Null if file creation fails.

Creates a new File instance from a *filepath.
filepath– aStringspecifying the full file path for the file to be created
Returns: a File object or Null if file creation fails.

Creates a new File instance from a *directoryPath and a fileName.
directoryPath– aStringspecifying the full file path for the containing directoryfileName– the name of the file to be created as aString
Returns: a File object or Null if file creation fails.

Creates a new File instance from the given fileUri.
fileUri– A fileURIspecifying the file
Returns: a File object or Null if file creation fails.

Tests if the given file is a directory.
file– aFiledenoting the file to be tested
Returns: A Boolean value.

Tests if the given file is a plain file and not a directory.
file– aFiledenoting the file to be tested
Returns: A Boolean value.

Returns child files the given file. If the given file is not a directory, an empty array is returned.
file– aFile
Returns: An Array of Files

Creates the non existing directories along the file path specified by the given file.
file– aFilespecifying a file path
Returns: A File if creation of directories succeeded, otherwise Null.

Reads the content of the given file to a JsonObject.
file– aFile
Returns: a JsonObject. If reading fails a Null is returned.

Reads the content of the given file to a ´String´.
file– aFile
Returns: A String. If reading fails a Null is returned.

Write the given string to the given file.
file– aFilespecifying the output filestring– aStringto be written
Returns: a Boolean indicating if file writing succeeded.

Write the given json to the given file.
file– aFilespecifying the output filejson– aJsonObjectto be written
Returns: a Boolean indicating if file writing succeeded.
Example
The usage of the functions of the File API is depicted in the following visual code example:
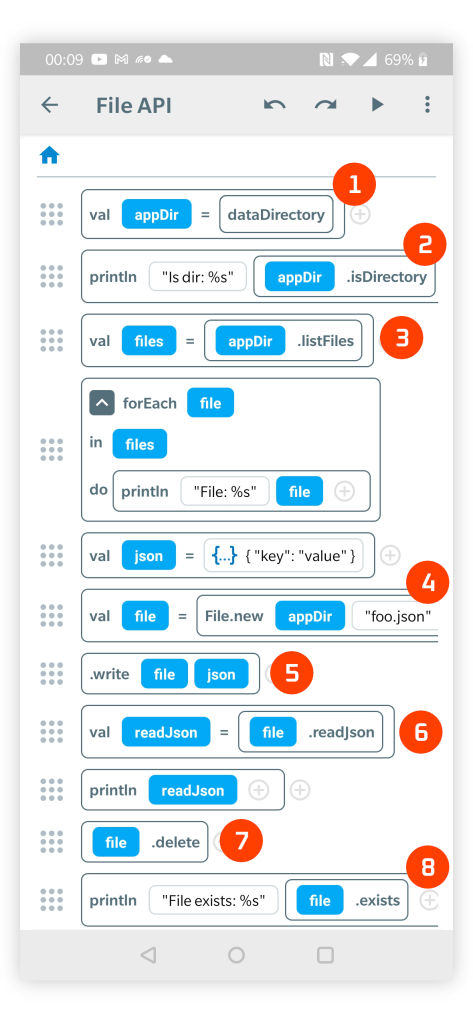
- dataDirectory function returns the application directory for writing and reading files.
- .isDirectory function tests if the given File is a directory. A similar function .isFile tests if a File is plain file and not a directory.
- .listFiles returns a list of child files (as an Array of Files) of the specified directory.
- File.new creates a new File object to represent a file inside the specified container directory.
- .write function writes the given JsonObject to a File. The function also supports writing any content as a String.
- .readJson reads file content of a given File as a JsonObject. There is also a .read function that reads the content of a file as a String.
- .delete removes the given File. It can be also used to recursively to delete a directory and all its contained files, so be careful with this function.
- .exists tests if the file specified by the given File exists.
- There is also .mkdirs function (not used in this example) that can used to create directories along the file path defined by a given File.
